Early stages of knee Osteoarthritis (OA) is characterised by the onset of pain and mild inflammation around the knee. Usually pain is more severe in the morning and the knee may feel stiff and take a while to loosen up.
What is Knee Osteoarthritis (OA)?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis and is characterised by the gradual breakdown of the articular cartilage in synovial joints, primarily of the knees, hands, and hips.
What causes Knee Osteoarthritis (OA)?
The body is complex and has processes in place to repair and maintain itself. OA is a result of this process being unable to occur correctly and causes an imbalance in enzymes which leads to the loss of collagen and proteoglycans, two proteins that are essential in the composition of the body's connective tissue. It can occur spontaneously or be secondary to another condition.
What are the Risk Factors for Knee Osteoarthritis (OA)?
OA is often associated with joint wear and tear due to aging but can also stem from joint injuries, musculoskeletal abnormalities, genetics, and environmental factors. Obesity exacerbates OA by increasing joint stress and inflammation.
What are the Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis (OA)?
Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion in the affected joint. Symptoms may worsen in cold weather, upon initiating activity, or after prolonged activity.
How is Knee Osteoarthritis (OA) Evaluated?
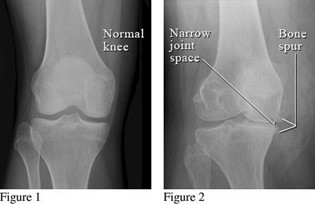
Practitioners diagnose OA using radiographic imaging. Key indicators of OA are narrowed joint spaces and bony spur formation which are indicative of cartilage breakdown.
What are the Treatment Options for Knee Osteoarthritis (OA)?
While there is no cure, treatment options aim to alleviate pain. Options include pharmaceuticals, physical therapy, bracing, and surgical intervention [1]. Treatment reccomendations will be tailored to the patietnt as well as the severity and location of the OA.
How Does Bracing Help Manage Knee Osteoarthritis (OA)?
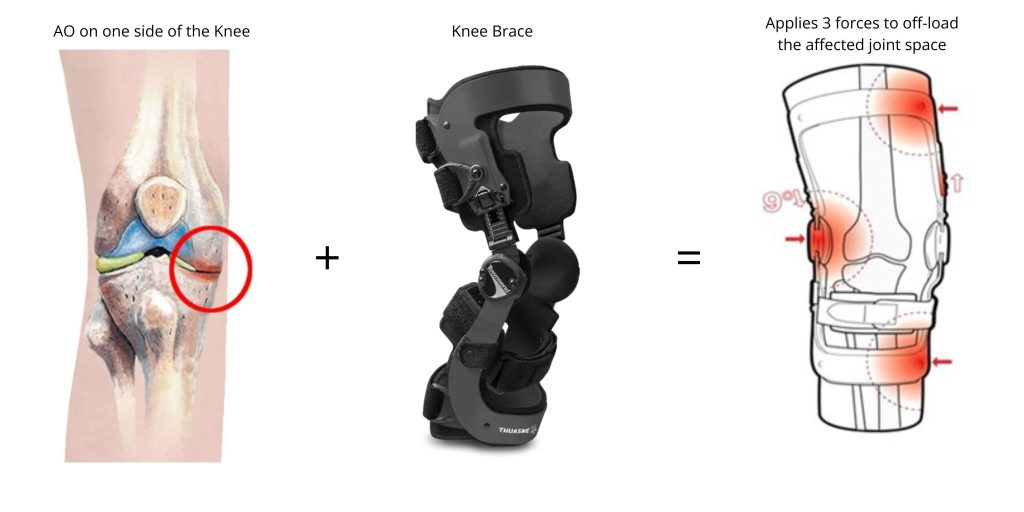
Bracing aims to offload or stabilize the affected joint to reduce pain[2,3]. It is often used alongside medication and can be effective for mild to severe OA. Braces will apply three forces, in a 'push' or 'pull' mechanism, to open the joint space and is primarily beneficial for unilateral OA.
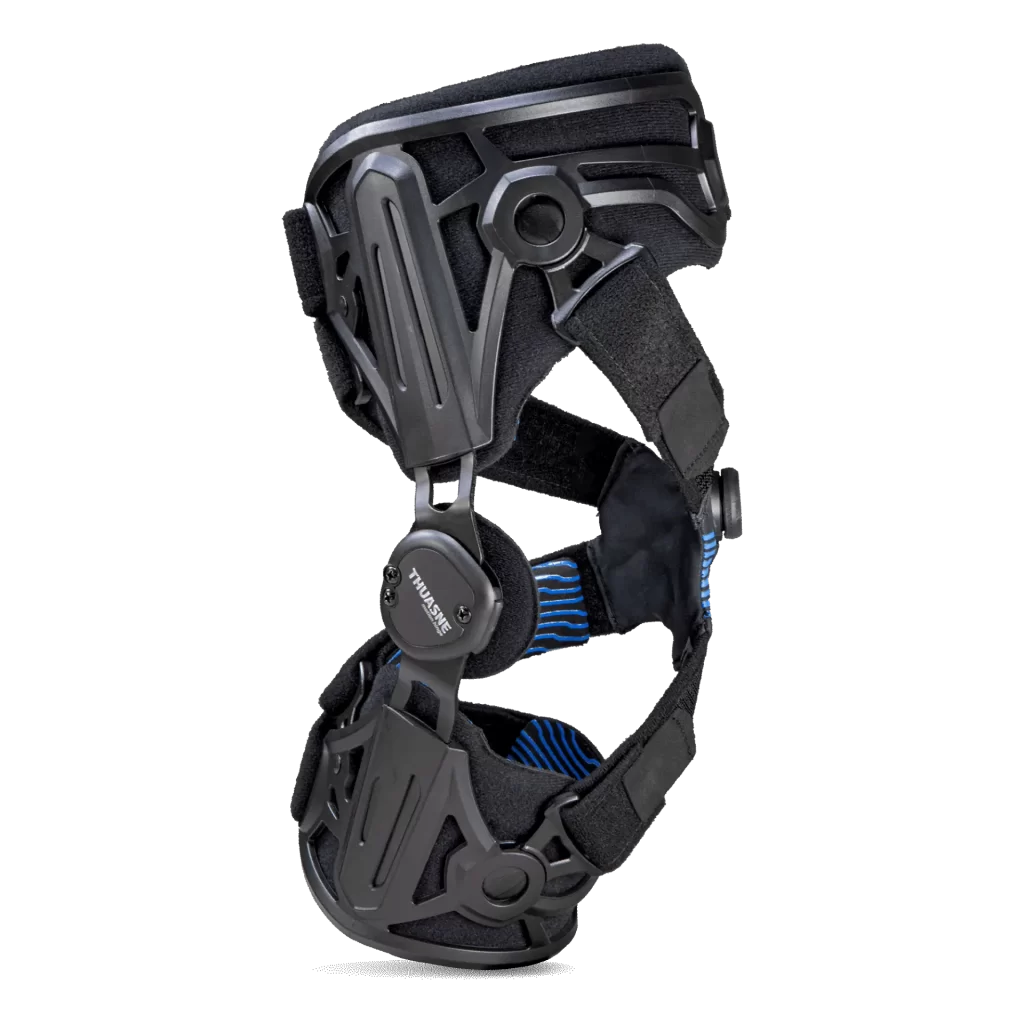
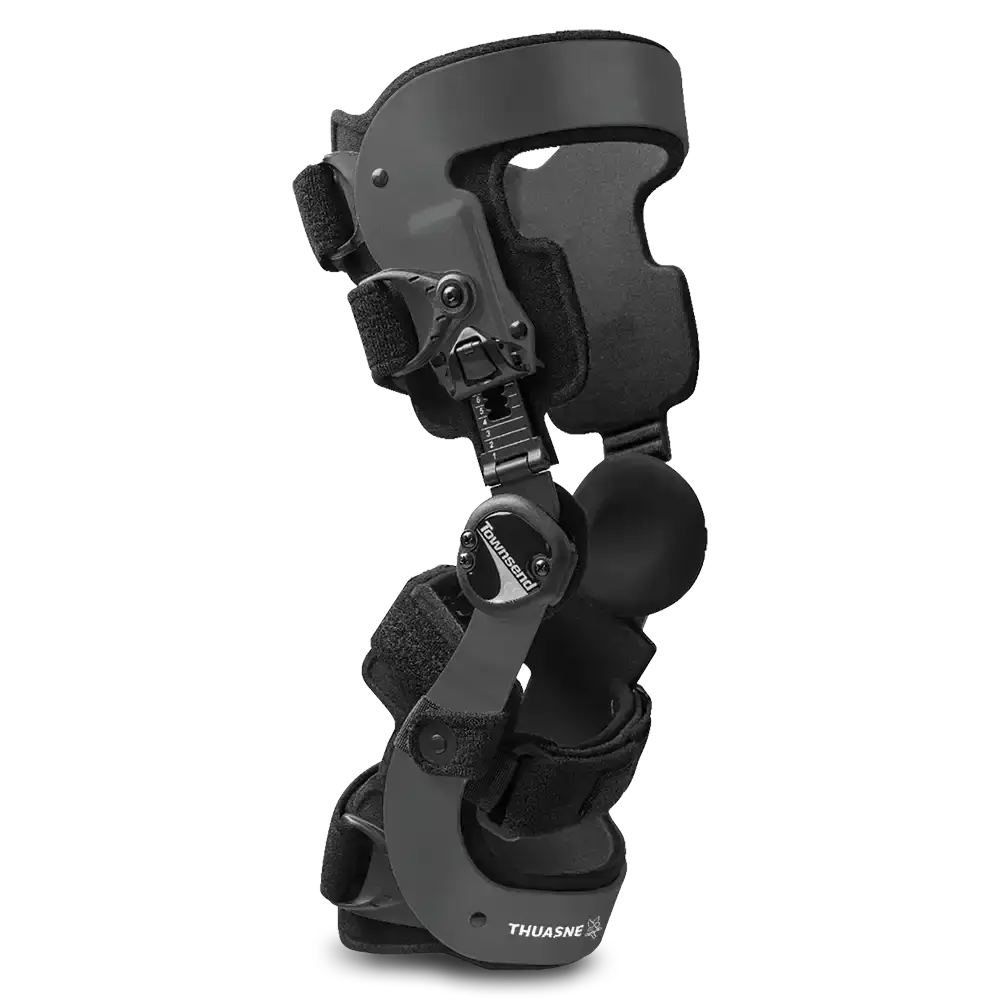
BRACING OPTIONS
The amount of support provided by the brace is dictated by the severity of the OA and how active a person is. For example, an individual with very severe OA but is not very active, will not require as much support as someone with the same level of OA but is very active. This is because the person who is not as active will not be putting as much weight through the joint which can aggrevate their condition.
Mild support
Recommended for individuals with low OA severity and high activity level or vice-versa.
Moderate support
Ideal for individuals with a moderate to high activity level or OA severity.
High support
For those with severe OA or a high activity level.
Please contact [email protected] for more information.
- DeRogatis, M., Anis, H. K., Sodhi, N., Ehiorobo, J. O., Chughtai, M., Bhave, A., & Mont, M. A. (2019). Non-operative treatment options for knee osteoarthritis. Annals of translational medicine, 7(Suppl 7), S245. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.06.68
- Cudejko T, van der Esch M, van den Noort JC, Rijnhart JJ, van der Leeden M, Roorda LD, Lems W, Waddington G, Harlaar J, Dekker J. Decreased pain and improved dynamic knee instability mediate the beneficial effect of wearing a soft knee brace on activity limitations in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis care & research. 2019 Aug;71(8):1036-43.
- Dries, T., VAN DER Windt, J. W., Akkerman, W., Kluijtmans, M., & Janssen, R. P. A. (2022). Effects of a semi-rigid knee brace on mobility and pain in people with knee Osteoarthritis. Journal of rehabilitation medicine. Clinical communications, 5, 2483. https://doi.org/10.2340/jrmcc.v5.2483
- Benning, R. Schneider-Nieskens. Superiority of a Knee Relief Orthosis in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Trial. ORTHOPÄDIE TECHNIK. 2017 Aug; 24-30.
- Lamberg EM, Streb R, Werner M, Kremenic I, Penna J. The 2-and 8-week effects of decompressive brace use in people with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. Prosthetics and Orthotics International. 2016 Aug;40(4):447-53.
- Thoumie P, Marty M, Avouac B, Pallez A, Vaumousse A, Pipet LP, Monroche A, Graveleau N, Bonnin A, Amor CB, Coudeyre E. Effect of unloading brace treatment on pain and function in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: the ROTOR randomized clinical trial. Sci Rep. 2018; 8: 10519.