What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) has become increasingly prevalent for workers who spend a majority of their work week on computers or in repetitive jobs, such as factory work or physical labour. It is a common condition that causes pain, weakness, numbness, tingling and reduced functionality in the hand and forearm. Symptoms are usually present in the palmar side of the hand and typically affect the thumb, index and middle fingers.
What Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The carpal tunnel is a passageway between the hand and forearm, formed by the carpal bones of the wrist and the transverse carpal ligament. It contains tendons as well as sensory and motor nerves. The median nerve provides sensation and innovation to the palmar side of the thumb,
index, middle and half of the ring finger. Over time, the median nerve can become compressed within the carpal tunnel, as a result of trauma, inflammation from conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis or repetitive use. During pregnancy, hormones can also cause fluid retention within the carpal tunnel.
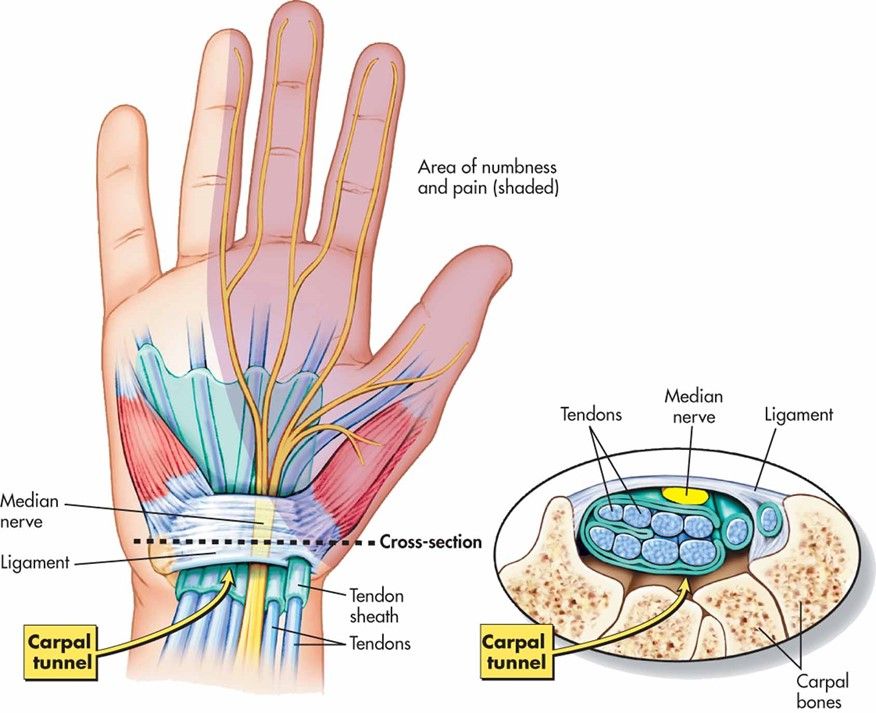
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome occurs when the median nerve is pinched as a result of trauma, increased pressure or blood supply issues (Genova, 2020). Increased pressure is the most frequent cause and commonly occurs due to excessive flexion and extension of the wrist (bending and extending). These movements increase the fluid pressure in the tunnel excessively and repetitive movements increase the risk for developing CTS.
Can I Use a Wrist Brace for Carpal Tunnel?
Bracing prevents the movement of the wrist and alleviates CTS symptoms. Immobilising the wrist reduces fluid pressure in the tunnel and the strain on the median nerve (Michlovitz et al., 2015). This has shown improvements in pain and hand function (Figueiredo, Ariboni, Tucci & Carvalho, 2024). Night-time wear of a wrist brace also reduces pain and increases functional outcomes (Burt. et al., 2015). Night splinting also prevents prolonged flexion (bending) of the wrist while you are asleep.
OPC Health wrist braces that immobilise the wrist & alleviate symptoms.
|
OPTIVOhand |
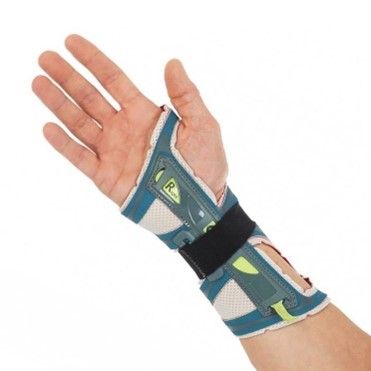 |
|
BioSkin DP2 & DP3 |
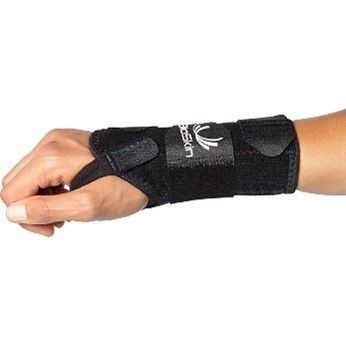 |
|
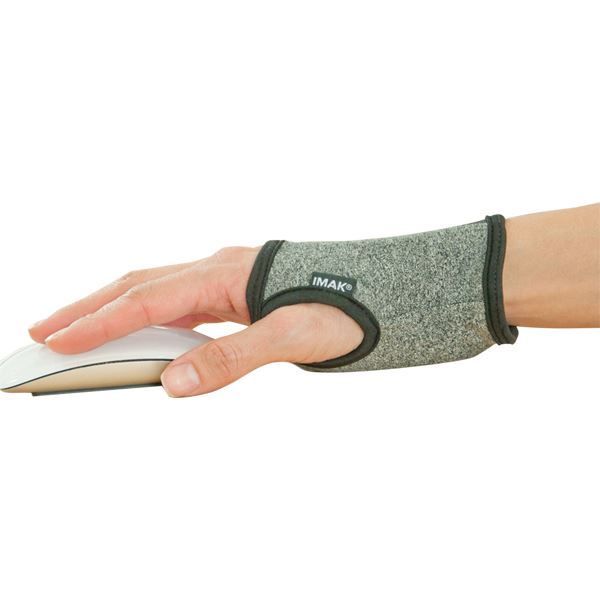
IMAK SmartGlove PM Carpal Tunnel Splint |
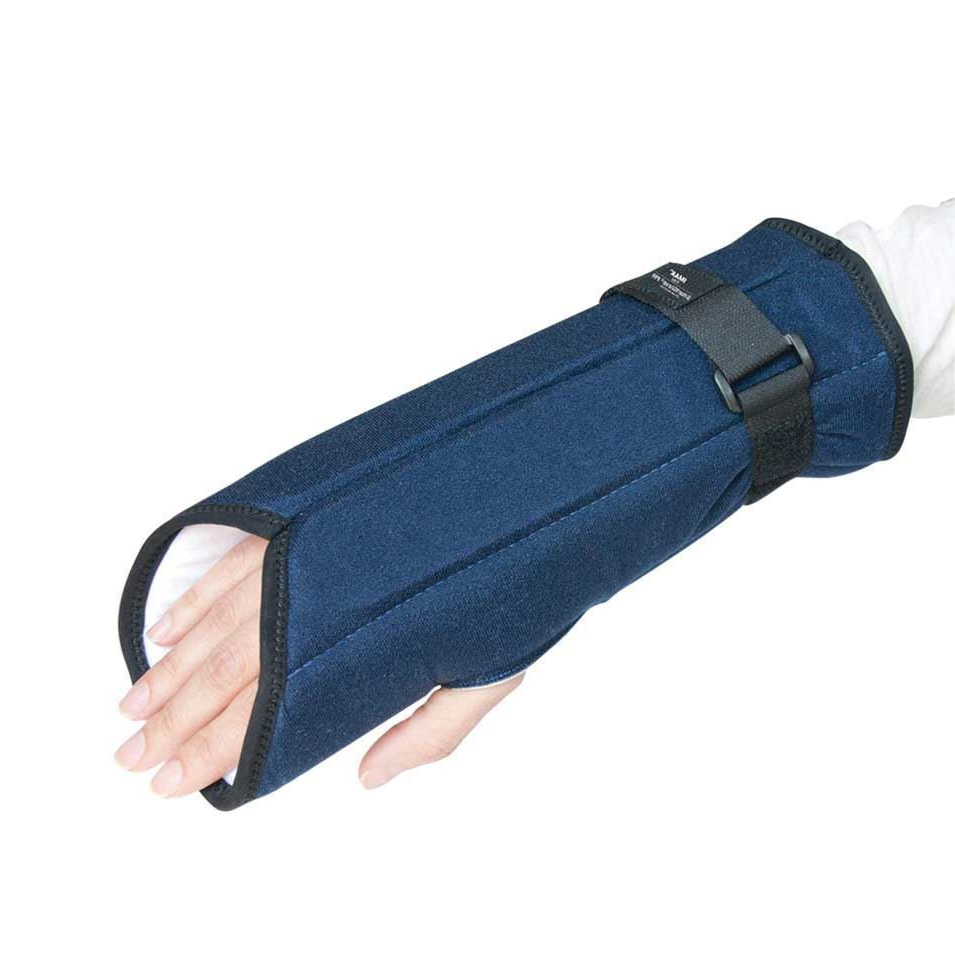 |
|
Futuro Night Wrist Support |
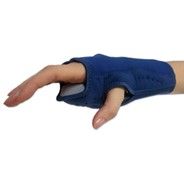 |
|
Actimove Manus Forte |
 |
|
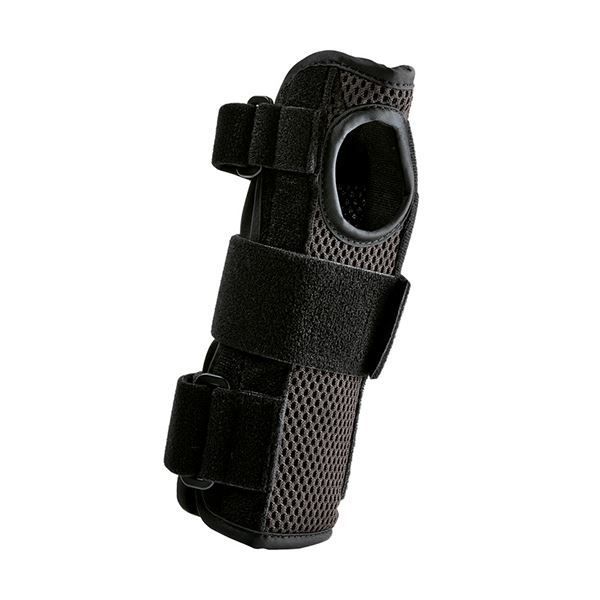
Uno-Who Wrist Brace |
 |
|
Wrist Lacer |
 |
|
Post Op Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Releases |
|
|
OPC GelFlex Wrist |
|
|
IMAK Computer Glove |
|
References
Burt, S., Dedlow, K., Francis, A., Gonczy, C., Johnson, S., Kadlec, A., ... & Porter, C. (2018). The effectiveness of nighttime wrist splinting for treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 48(7), 558-566.
Figueiredo DS, Ariboni RR, Tucci HT, Carvalho RP. Effects of wrist orthoses in reducing pain in individuals with carpal tunnel syndrome: a systematic review. Disabil Rehabil. 2024 Jan 12:1-9. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2023.2301019. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38217327.
Genova, A., Dix, O., Saefan, A., Thakur, M., & Hassan, A. (2020). Carpal tunnel syndrome: a review of literature. Cureus, 12(3).
Michlovitz, S. L., Harris-Love, M. O., & Whilte, L. (2015). Orthotic intervention for carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Hand Therapy, 28(1), 31-38.